
Neurofeedback
About QEEG
Quantitative Electroencephalography (e-lec-tro-enceph-a-lo-graphy-EEG) QEEG is a neurological diagnostic procedure that measures and records the changes in electrical potentials (cortical activity/brainwaves), in various parts of the brain. Measures are taken at the surface of the scalp, using digital technology. A multi-electrode recording of brain wave activity is recorded and converted into numbers , and these numbers are then statistically analyzed and are converted into a color map of brain functioning.
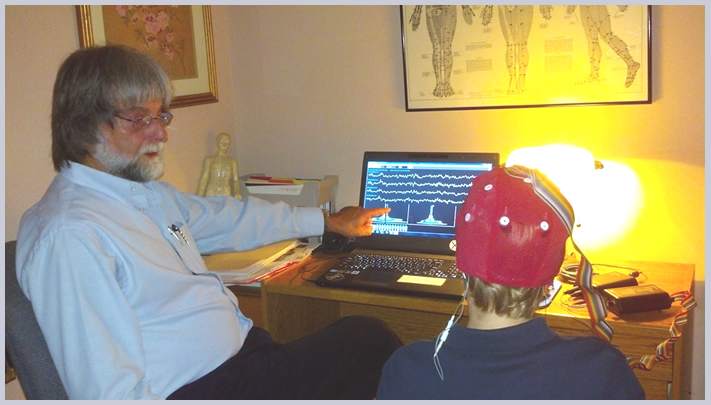
By recording the electrical activity of the brain from the scalp, EEG images the brain by taking measures with both eyes closed and eyes opened; and may also be done while the patient is performing a cognitive task. This allows for detection of the location and magnitude of brain activity involved in the various types of cognitive functions. Images are acquired by placing a cap with electrodes on the head or by using individual electrodes to monitor the amount of electrical activity at different points on the scalp.
The QEEG mapping system used for this mapping is the New Mind Maps Magnitude Analysis System. The Magnitude Analysis System provides a reference database system that provides simple output indicating whether EEG is high or low in the various dimensions of analysis.

A QEEG consists of placing a cap with twenty electrodes/sensors on the patient's head, and ear clips on each ear lobe. Each site will first be cleansed and electrode paste/gel will be placed under each sensor to insure proper conductivity to read the patient's brainwaves. The recording is done while the patient is in a reclining chair. The patient is asked to relax with eyes closed and a second set of measures is taken with eyes opened. Preparation takes approximately 20-30 minutes and the actual EEG recordings take about 15-20 minutes.
The benefits of QEEG include but are not limited to assessing overall brain function that includes magnitude (power) connectivity (brain functioning) and asymmetry (the balance of certain brain waves). In addition the QEEG will produce an analysis of cognitive functioning, an emotional analysis, a list of supplements that may be deficient and a list of metabolic categories. QEEG cannot be used for diagnostic purposes; however, it may be used for differential diagnosis. QEEG helps assess the patient's need for specialized treatment.
QEEG provides an analysis of brain functioning. There are generally no risks involved with QEEG. In some cases patients may feel anxious about having the procedure done. There are no known side effects. Alternative methods of determining brain functioning include but are not limited to Medical EEG, MRI, fMRI, brain scans including CAT and SPECT.
Often, professionals will ask, how does EEG compare to other measures?
- EEG can invalidate MRI.
- PET and fMRI provide better spatial resolution than EEG and MEG (magnetoencephalography), but poorer temporal resolution. MRI shows responses in terms of seconds while EEG shows responses in terms of milliseconds.
QEEG Brain Maps and Disorders
Brain maps have become progressively more utilized in diagnosis and training strategies in recent years. Their validity for diagnostic purposes is still hotly debated in the field of neurology, but they have been used for a variety of purposes for many years. One has only go to PubMed and use the search term QEEG to uncover the thousands of research papers that have used QEEG. However, recent research continues to bring QEEG brain mapping closer to the realm of diagnostic ability.
QEEG-guided neurofeedback is likely to be the standard in the future. Until recently, it has been mistakenly seen primarily as a method for deriving protocols. It has not proven to be the best and only valid method for all neurofeedback cases in a clinical setting.